
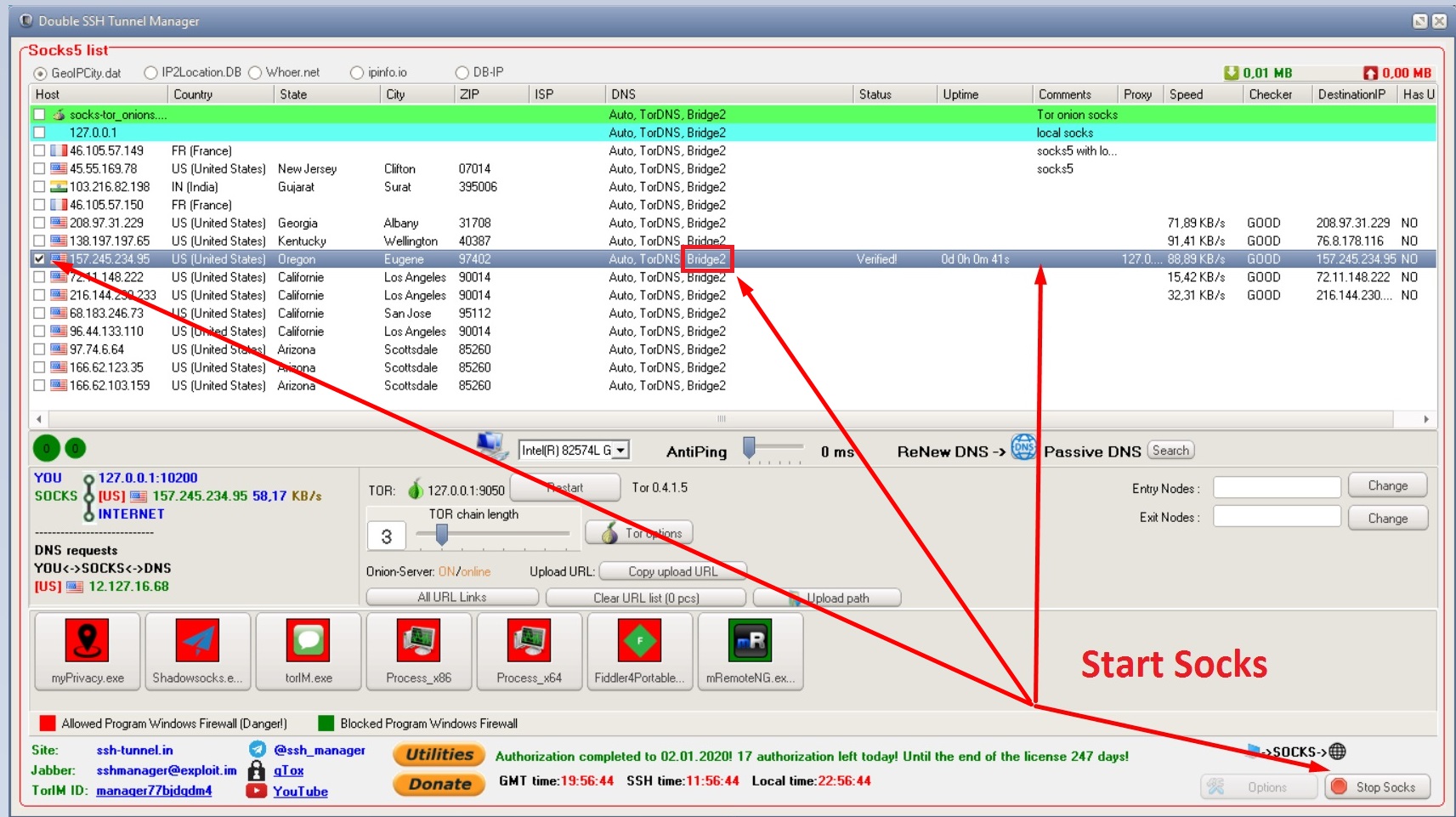
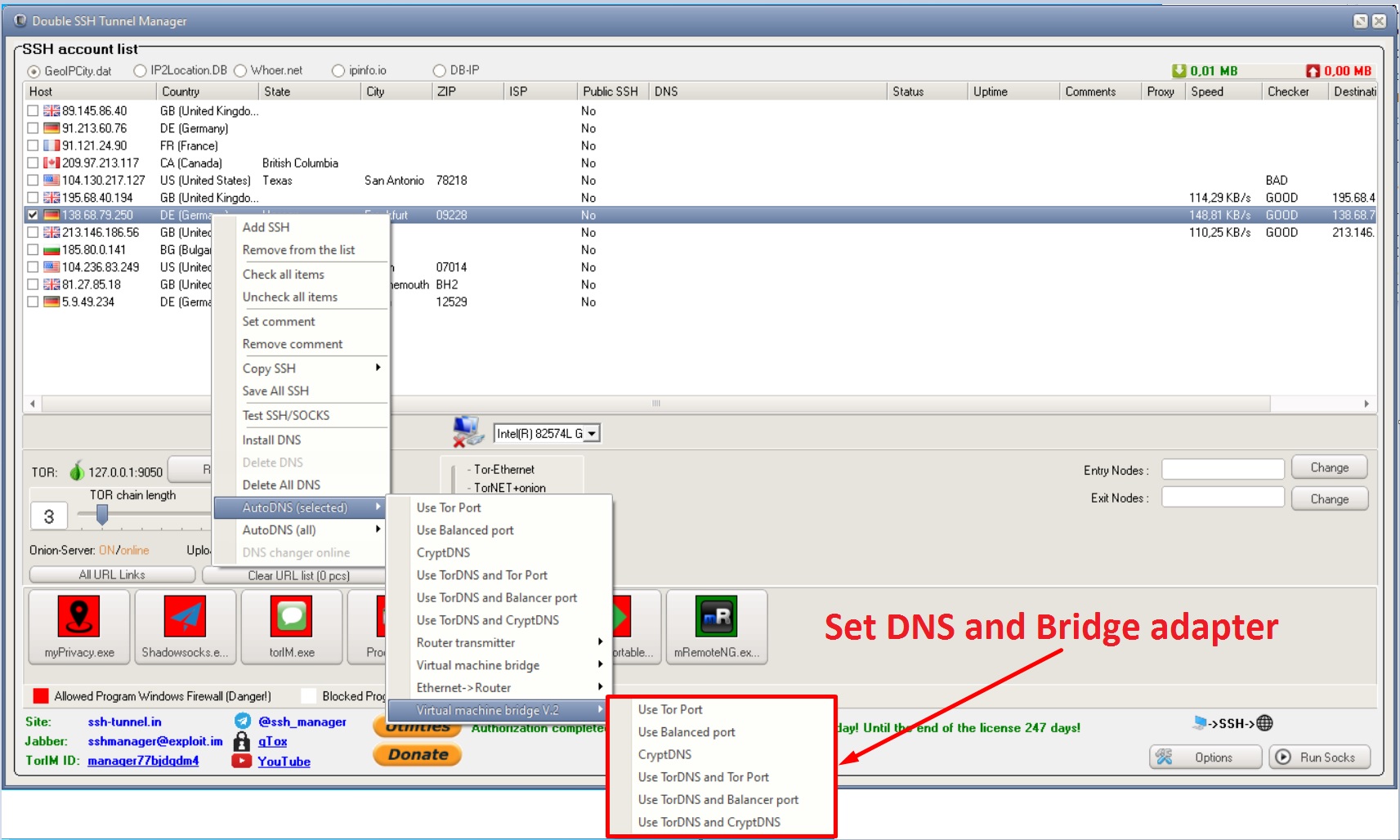
Update ~/.ssh/config file (older method with netcat )Įdit the $HOME/.ssh/config file using a text editor such as vi, enter: It can be used to pass connections to a 2nd server such as FooServer.
In this example, the utility netcat (nc) is for reading and writing network connections directly. Now, my laptop (local system) is connected to Jumphost it now connected FooServer. The netcat (nc) command is needed to set and establish a TCP pipe between Jumphost (or firewall) and FooServer. $ ssh -t -o Prox圜ommand='ssh nc FooServer 22' htop $ ssh -o Prox圜ommand='ssh nc FooServer 22' -t option is needed to run commands # $ ssh -o Prox圜ommand='ssh firewall nc remote_server1 22' remote_server1 The syntax is as follows and works with all clients $ ssh nixcraftserver3 Say hello to the Prox圜ommand with netcat (older method) IdentityFile /home/vivek/.ssh/nixcraftserver3_e25519 IdentityFile /home/vivek/.ssh/nixcraftserver2_e25519 IdentityFile /home/vivek/.ssh/nixcraftserver1_e25519 o 'Prox圜ommand ssh -l jerry %h nc 22' \Īn updated version of my ~/.ssh/config file: The user ‘jerry’ is the account on the intermediary or jump host: $ ssh -l tom \ Here, ‘tom’ is the account on the second machine which is the final target. Say the user accounts names are different on the two Unix or Linux server. You no longer need nc installed due Prox圜ommand syntax:
#Double ssh tunnel manager download how to
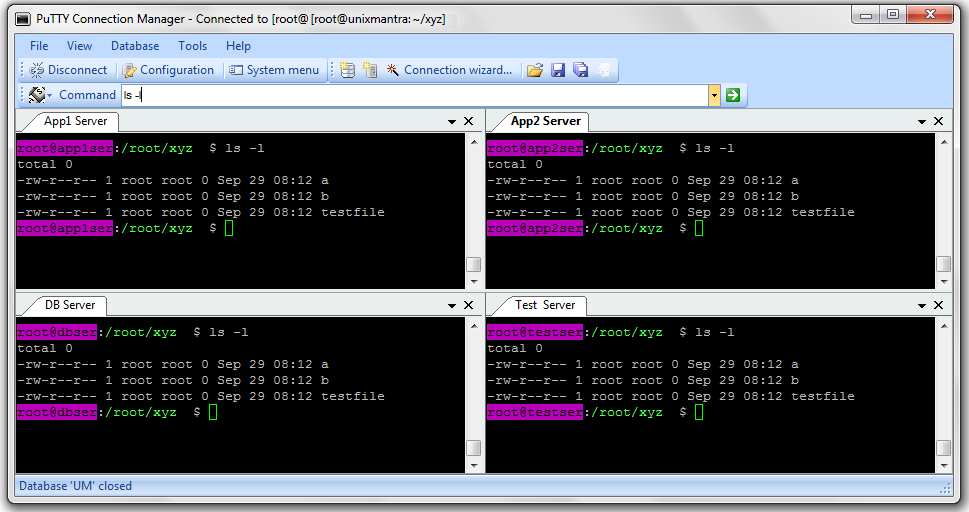
How to pass through a gateway using stdio forwarding Multiple -tt options force tty allocation, even if ssh has no local tty. This can be used to execute arbitrary screen-based programs on a remote machine.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
